The FDIC today issued the list of 71 enforcement actions taken against banks and individuals in December 2012. In the previous month, there were a total of 72 enforcement actions taken.
The December enforcement actions include the following:
- 11 consent orders
- 1 prompt corrective action
- 13 civil money penalties
- 12 section 19 orders
- 14 orders terminating consent orders and cease and desist orders
- 17 removal and prohibition orders
Consent orders are issued to banks considered to be operating in an unsafe and unsound manner and is one of the most serious regulatory actions that can be taken against a bank under Section 8 of the Federal Deposit Insurance (FDI) Act.
According to the FDIC “the FDIC attempts to obtain a Consent Cease and Desist Order in an effort to eliminate the need for time consuming administrative hearings. The Consent Cease and Desist procedure is premised upon agreement to a stipulation between the representatives of the FDIC and the bank’s board of directors whereby the bank agrees to the issuance of a Cease and Desist Order without admitting or denying that any unsafe or unsound practices and/or violations of law or regulation have occurred. The effect of this procedure is to reduce the time period between initial review of the case and the date on which an enforceable and binding Cease and Desist Order is issued.”
A Prompt Corrective Action Directive (PCAD) is the most serious action that can be taken against a bank and requires immediate corrective action to be taken by the bank. Typically, a PCAD issued to a bank is a strong indicator of imminent failure.
FDIC guidelines on issuing a PCAD state that “Prompt corrective action is a framework of supervisory actions for insured depository institutions which are not adequately capitalized. These actions become increasing severe as an institution falls within lower capital categories.”
The one PCAD issued in December was issued against First South Bank of Spartanburg, South Carolina. First South Bank has a very high troubled asset ratio of 360%. Historically, once a bank exceeds a troubled asset ratio of 100%, failure of the bank becomes almost inevitable.
Section 19 orders issued under the provisions of Section 19 of the FDI Act are issued by the FDIC to prohibit any person convicted of “any criminal offense involving dishonesty or breach of trust” from participating in the control or management of an FDIC insured institution.
Civil money penalties are assessed against banks or individuals found to be in violation of various rules and regulations.
Removal and prohibition orders are usually taken by regulators against individuals who have committed “violations of law or regulations, unsafe or unsound banking practices, and/or breach of fiduciary duty.” An individual issued a removal and prohibition order is banned from any further participation in the affairs of any financial institution insured by the FDIC.
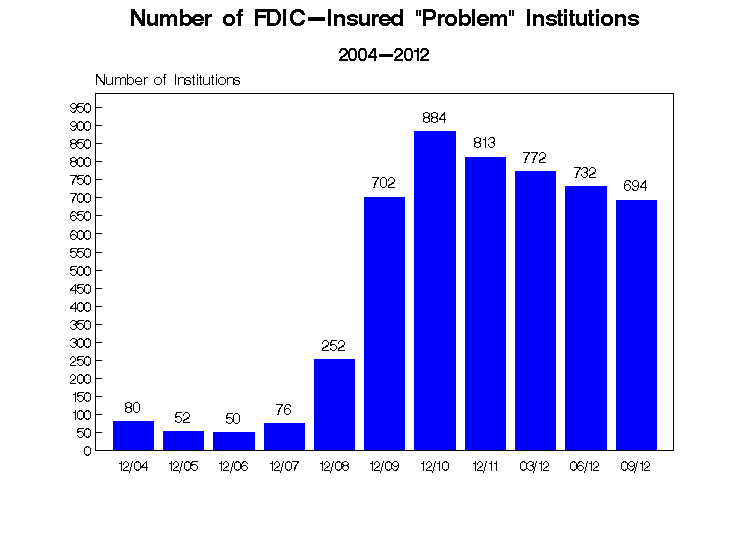
Despite the stabilization of the banking industry, almost one out of every ten FDIC insured institutions is still classified as a Problem Bank by the FDIC. Virtually all of the problem banks have outstanding enforcement actions issued against them. At September 30, 2012, there were 694 banks on the FDIC Problem Bank List out of a total of 7,181 FDIC insured banks and savings institutions.
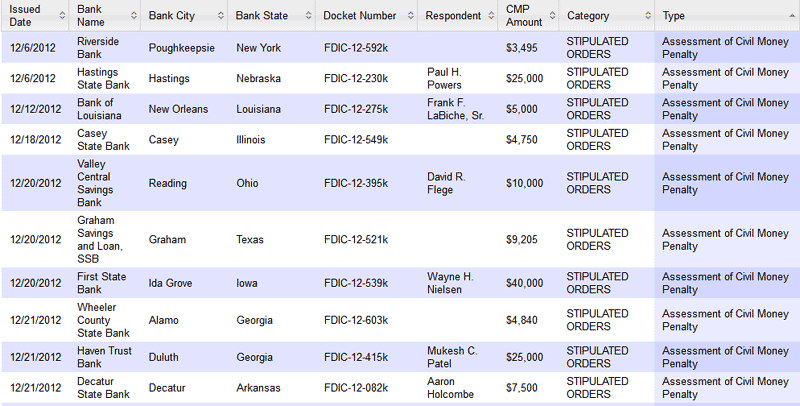
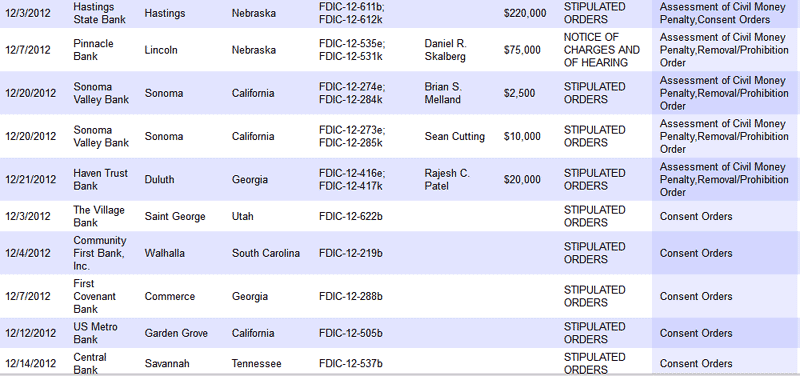
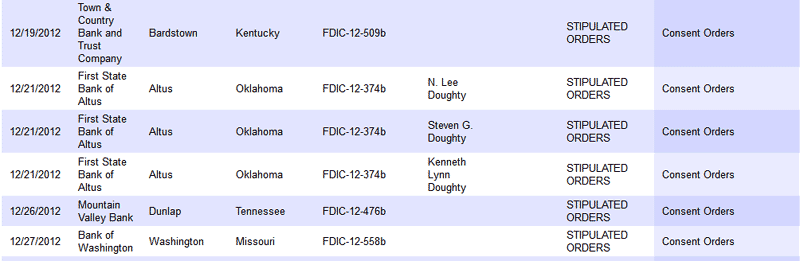
 Banks issued civil money penalties, consent orders and prompt corrective action notices are listed below. The full listing of December enforcement actions can be viewed at FDIC Enforcement Decisions and Orders.
Banks issued civil money penalties, consent orders and prompt corrective action notices are listed below. The full listing of December enforcement actions can be viewed at FDIC Enforcement Decisions and Orders.
Are any of these banks looking for private equity groups or real estate investment trusts to help them out through buying distressed assets? If so, contact me. I’m not hard to find.