 The FDIC issued a list of 40 enforcement actions taken against banks and individuals during March 2014. The enforcement actions include the following:
The FDIC issued a list of 40 enforcement actions taken against banks and individuals during March 2014. The enforcement actions include the following:
- 4 consent orders
- 1 prompt corrective action directive
- 9 section 19 orders
- 14 orders terminating consent orders and cease and desist orders
- 1 order terminating a prompt corrective action
- 2 civil money penalties
- 6 removal and prohibition orders
The most serious enforcement actions are consent orders and prompt corrective actions directives.
Consent orders are issued to banks considered to be operating in an unsafe and unsound manner and is one of the most serious regulatory actions that can be taken against a bank under Section 8 of the Federal Deposit Insurance (FDI) Act.
The four consent orders issued in March were against the following banks:
- Marathon Savings Bank, Wausau, Wisconsin
- The West Michigan Savings Bank, Bangor, Michigan
- International Bank of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois
- New Jersey Community Bank, Freehold, New Jersey
A Prompt Corrective Action Directive (PCAD) is the most serious action that can be taken against a bank and requires immediate corrective action to be taken by the bank. Typically, a PCAD issued to a bank is a strong indicator of imminent failure.
FDIC guidelines on issuing a PCAD state that “Prompt corrective action is a framework of supervisory actions for insured depository institutions which are not adequately capitalized. These actions become increasing severe as an institution falls within lower capital categories.”
The one PCAD issued in March was issued against Columbia Savings Bank, Cincinnati, Ohio. Columbia Savings Bank has a very high troubled asset ratio of 328%. Historically, once a bank exceeds a troubled asset ratio of 100%, failure of the bank becomes almost inevitable.
Section 19 orders issued under the provisions of Section 19 of the FDI Act are issued by the FDIC to prohibit any person convicted of “any criminal offense involving dishonesty or breach of trust” from participating in the control or management of an FDIC insured institution.
Civil money penalties are assessed against banks or individuals found to be in violation of various rules and regulations.
Removal and prohibition orders are usually taken by regulators against individuals who have committed “violations of law or regulations, unsafe or unsound banking practices, and/or breach of fiduciary duty.” An individual issued a removal and prohibition order is banned from any further participation in the affairs of any financial institution insured by the FDIC.
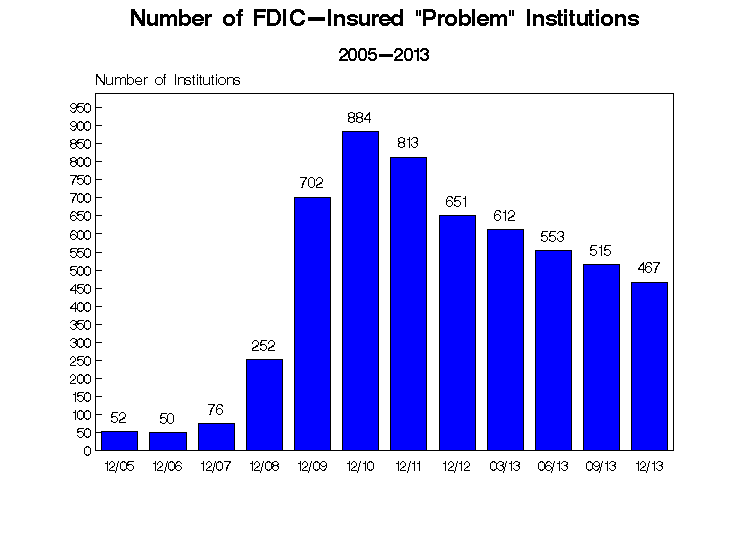
Despite the sharp decline in banking failures over the past two years, there are still 467 banks on the FDIC’s confidential Problem Bank List at December 31, 2013, representing 6.9% of the 6,812 banking institutions insured by the FDIC. Virtually all of the problem banks have outstanding enforcement actions issued against them.
 Since 2008 a total of 495 financial institutions have failed.
Since 2008 a total of 495 financial institutions have failed.
Banking Failures Since 2008
Year Number of Bank Failures
2008 25
2009 140
2010 157
2011 92
2012 51
2013 23
2014 6
Total 495
The entire list of FDIC enforcements actions for March can be viewed at FDIC Enforcement Decisions and Orders.
How do I find out if the FDIC has issued any consent orders against First National bank of Chatsworth, GA? I know it is not publicly traded, so how do I find out who owns that bank?
The unofficial Problem Bank List contains the names of all banks that have been issued enforcement actions.
Information on specific FDIC insured institutions can be found at BankFind on the FDIC web site.